E-Commerce exports from India: The engine for USD 1 trillion goods exports by 2030 – Part 1
This is the first part in the two part series where we shall look at the e-commerce exports from India. The first part sets the context, and the second part delves into the policy and regulatory aspects. The post was first published at Swarajya magazine at: https://swarajyamag.com/economy/this-category-in-e-commerce-can-fuel-indias-journey-to-1-trillion-in-exports-by-2030
India has set a goal of reaching USD 2 trillion in exports by 2030 - 1 trillion of this amount from exporting goods/merchandise and 1 trillion from services exports. This target was announced on the back of a record 776 billion USD of total exports achieved during FY23 – out of which USD 451 billion came through export of goods and USD 325 billion through services. This financial year (FY24), though, because of global challenges, the combined exports in goods and services during April-Jan 2024 have remained stagnant at around USD 640 Billion, and it’s expected that the total exports would remain in the same ballpark. The target for 2030 therefore has become stiffer.
“Each district of our country has a potential equal to that of one country, each of our districts has the capacity equal to a small country in the world. Why should each district not think of becoming an export hub? Each of our districts has a diverse identity and potential for global market.”
To appreciate the profound significance of the statement, it's essential to delve into specific data points. The first data point of interest focuses on the cumulative value of exports from the districts.
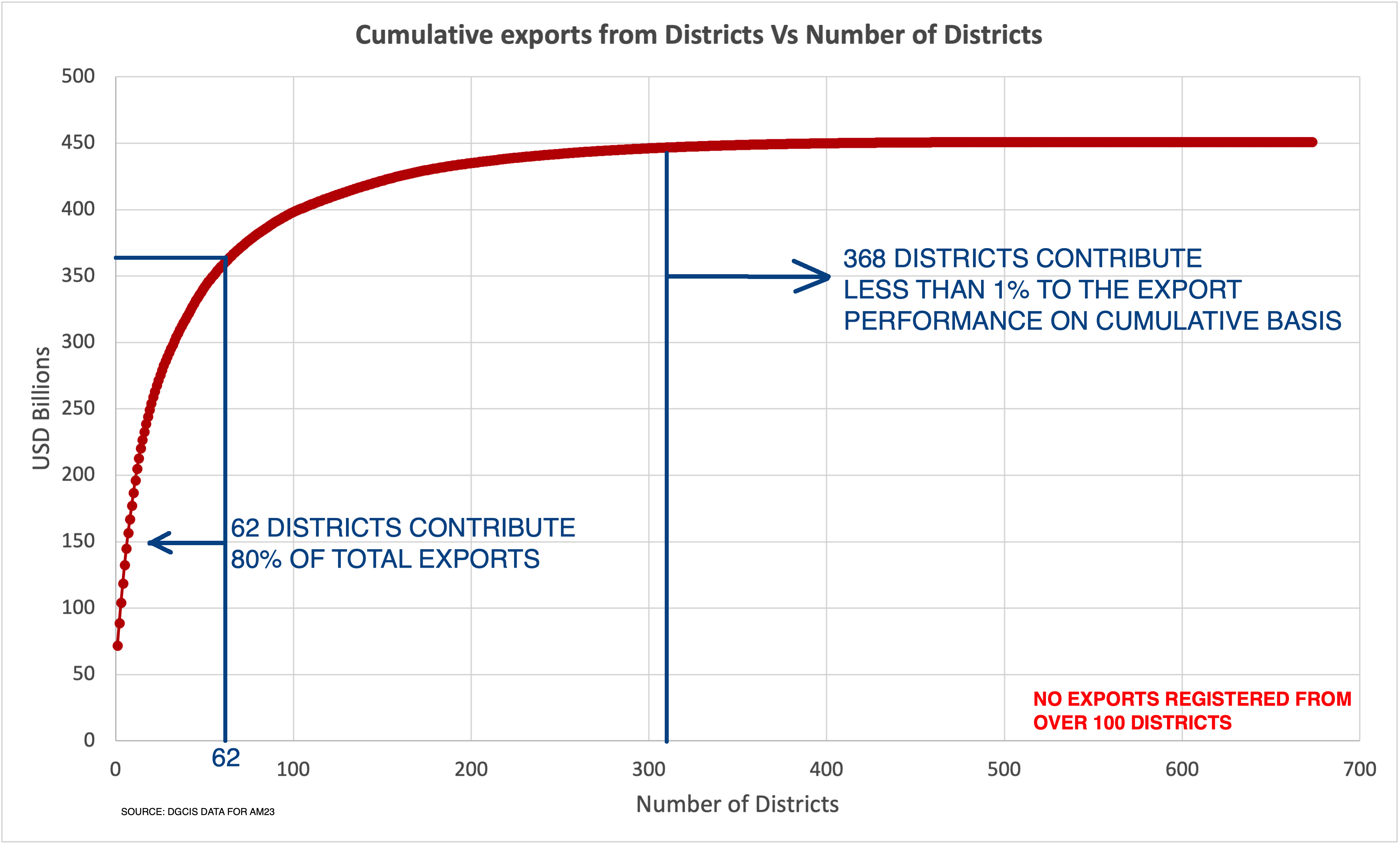 |
| Fig: Lion's share of exports from handful of districts |
According to the data for FY April’22-March’23, 10% of our districts account for over 80% of our exports. There are around 100 districts that do not export. Even among those that do, there are over 350 districts that together make up less than 1% of total exports. This is where the importance of Prime Minister’s statement comes into picture. Unless most districts perform, we will not be able to ramp up exports meaningfully and inclusively. And not all these districts can become an automobile hub or host an electronics hardware park. Therefore, one needs to look beyond the traditional export products, and stretch the existing export ecosystem framework to include products that are not exported in the current ecosystem. This has started happening through cross-border E commerce exports where goods are being sold online, using digital medium, directly to consumers and businesses abroad.
To answer this, we need to delve into the Harmonized System (HS) of trade classification, which categorizes goods into 99 chapters at the 2-digit level. The initial chapters, 01 to 24, encompass primary agricultural products and their processed derivatives. In contrast, chapters towards later parts from 80 onwards cater to fields like engineering, automobiles, and electronics—sectors traditionally linked with significant capital investment and global value chains, including mobile phones, electronics, automobiles, and aircraft.
Among the chapters, we can broadly identify sectors inherently suitable for MSMEs—such as toys, textiles, leather, food products, wood and glassware, brass and metal ware, handicrafts, and handlooms, ayurvedic medicines and preparation, among others. These areas, characterized by their potential for artisanal and small-scale production, are particularly poised for leveraging e-commerce for global outreach, when compared against heavy industries (petroleum, chemicals or steel) or sectors falling under global value chains (electronics, large consumer appliances). This brings us to the second data point.
 |
| Fig: Overall sector and the box of opportunities |
In the visual depicted above, the most extensively traded commodities are positioned towards the right, with the bubble's size reflecting the export value of each item from India during FY23. One may notice the era's defining globalization trend, where most of these globally traded goods, with share of over 5% in global trade, are those that are integrated into supply chains overseen by multinational corporations. These high volume items, and petroleum products, contribute almost three fourths of the total global trade. Currently, India's contribution to the trade of these high-volume items remains modest at 1.4% (CY22). Strategic initiatives focused on bolstering the manufacturing sector—underscored by policies like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, PM-MITRA, and significant infrastructure enhancements—are in motion to alter this dynamic. However, the area of interest for E-Commerce growth are the commodities highlighted within the rectangular box of opportunities, revealing insights into potential areas for growth and increased participation in the global trade ecosystem. If we zoom into the box, we see the visual below.
 |
| Fig: The box of opportunities that can be leveraged in e-commerce |
In this 'box of opportunities', we can identify many sectors ripe for MSME engagement yet markedly underrepresented in global trade. As previously discussed, the x-axis represents the share of the item in world trade as a percentage, while the y-axis denotes India's share in world exports as a percentage. This zoomed-in view focuses on the 'Box of Opportunities' where sectors inherently suitable for MSMEs are represented. These sectors, with a share in the global market below 1%, and India's share in global trade of these items under 5%, represent areas of untapped potential. Easily identifiable among them are the wood and handicrafts, toys and sports goods, ceramics, apparel and textile, leather products, footwear, miscellaneous metal and non-metal manufactured items etc. E-commerce emerges as a crucial enabler for such sectors, providing MSMEs with a viable entry point to compete on the international stage. Though these commodities individually account for a modest portion of global trade, collectively, they represent a market size exceeding USD 6 trillion per annum (CY2022), which is a quarter of the total global trade. India has a share of 1.4% in the global trade for the items which are within the box of opportunities. This points to a great scope for improvement. To contrast, China’s exports of these items constitute around 16% of the global market. Capturing an additional 10% of this market through supportive measures for MSMEs in the coming years could yield an incremental export of USD 600 billion from India. A significant portion of that can come through e-commerce. A good example of this possibility are Coir products (chapter 53) and Carpet industry (Chapter 57) in which India has a share of around 10% in the world market and we can no longer see them in the box.
As we explore the growth potential of e-commerce exports from India, it's important to note that we are focusing on a specific subset of cross-border e-commerce exports where goods are digitally ordered, paid for, and physically delivered across borders. This subset presents ample opportunities to diversify and make trade more inclusive.
Quantifying the exact volume of goods exported from India through e-commerce channels is challenging due to limitations in data collection mechanisms. Despite this, estimates suggest that India's e-commerce exports ranged between USD 2 to 5 billion during the fiscal year 2022-23, highlighting the need for more sophisticated tracking and reporting mechanisms. China, the current world leader in cross-border e-commerce, exported USD 230 billion in 2022 (WTO estimate).
The global market for e-commerce exports is poised for exponential growth, with projections indicating a potential surge from USD 800 billion in 2022 to USD 8 trillion by 2030 (GTRI). India is well-positioned to capitalize on this trend, underscoring the importance of strategic initiatives and policies to enhance its competitiveness.
The Prime Minister's vision of districts becoming export hubs emphasizes the importance of leveraging e-commerce exports to tap into the local potential and diversity of each district, enabling MSMEs, artisans, and craftsmen to access international markets without heavy investments or intermediaries. E-commerce exports can help overcome traditional barriers faced by Indian exporters, serving as a key driver for achieving the goal of USD 1 trillion in goods exports by 2030.
In the next part, we will discuss the regulatory and policy reforms needed to achieve this vision and the paradigm-shifting changes happening in this sector that may affect the future of international trade.
Comments
Post a Comment
Comments are moderated. Your comment will be online shortly. Kindly excuse the lag